Click here to go the previous part of this article – Introduction
Prerequisites (important – have the prerequisites ready before you start the SharePoint 2010 install!)
i. Hardware
Verify that you have the following server virtual or physical hardware architecture available to you [2]:
1. Application Server
a. Processor 64-bit, four cores (*64 bit is the key, it won’t run on 32 bit architectures)
b. Recommend 16 GB or Higher RAM
c. 80 GB Hard drive for main system drive
2. Web Server (s)
a. Processor 64-bit, four cores (*64 bit is the key, it won’t run on 32 bit architectures)
b. Recommend 16 GB or Higher RAM
c. 80 GB Hard drive for main system drive
3. Database Server(s)
a. Processor 64-bit, four cores (*64 bit is the key, it won’t run on 32 bit architectures)
b. Recommend 16 GB (at a minimum) or Higher RAM
c. Preferably a cluster
d. Dependent on your usage type – a very large hard drive or the databases (recommend 1 TB on a SAN)
iiii. Software
Verify that you have the following software installed or available to you. Please visit the Microsoft website for more complete descriptions but below is a summary [2]:
1. Application Server
a. One of the following OS’s
i. 64-bit edition of Windows Server 2008 Standard, Enterprise, Data Center, or Web Server with SP2 [7] Operating system
1. You also need a hotfix [8]
ii. 64-bit edition of Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard, Enterprise, Data Center, or Web Server
1. You also need a hotfix [9]
b. All Windows Updates
c. If you would like to have the SharePoint server take in incoming email into lists, you should have SMTP service installed on your Windows Server OS
d. Optional – The following prerequisites are automatically installed with the SharePoint 2010 media, however, you can install them yourself if you like beforehand:
i. Web Server (IIS) role
ii. Application Server role
iii. Microsoft .NET Framework version 3.5 SP1
iv. SQL Server 2008 Express with SP1
v. Microsoft Sync Framework Runtime v1.0 (x64)
vi. Microsoft Filter Pack 2.0
vii. Microsoft Chart Controls for the Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5
viii. Windows PowerShell 2.0
ix. SQL Server 2008 Native Client
x. Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services ADOMD.NET
xi. ADO.NET Data Services Update for .NET Framework 3.5 SP1
xii. Windows Identity Foundation (WIF)
2. Web Server (s)
a. One of the following OS’s
i. 64-bit edition of Windows Server 2008 Standard, Enterprise, Data Center, or Web Server with SP2 [7] Operating system
1. You also need a hotfix [8]
ii. 64-bit edition of Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard, Enterprise, Data Center, or Web Server
1. You also need a hotfix [9]
b. All Windows Updates
c. If you would like to have the SharePoint server take in incoming email into lists, you should have SMTP service installed on your Windows Server OS
d. Optional – The following prerequisites are automatically installed with the SharePoint 2010 media, however, you can install them yourself if you like beforehand:
i. Web Server (IIS) role
ii. Application Server role
iii. Microsoft .NET Framework version 3.5 SP1
iv. SQL Server 2008 Express with SP1
v. Microsoft Sync Framework Runtime v1.0 (x64)
vi. Microsoft Filter Pack 2.0
vii. Microsoft Chart Controls for the Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5
viii. Windows PowerShell 2.0
ix. SQL Server 2008 Native Client
x. Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services ADOMD.NET
xi. ADO.NET Data Services Update for .NET Framework 3.5 SP1
xii. Windows Identity Foundation (WIF)
3. Database Server(s)
a. One of the following OS’s
i. 64-bit edition of Windows Server 2008 Standard, Enterprise, Data Center, or Web Server with SP2 [7] Operating system (I think that Windows 2003 64 bit might work for ONLY the SQL Server as well but I’m not sure)
1. You also need a hotfix [8]
ii. 64-bit edition of Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard, Enterprise, Data Center, or Web Server
1. You also need a hotfix [9]
b. All Windows Updates
c. One of the following version of SQL Server
i. 64-bit edition of Microsoft SQL Server 2008 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) [3] and Cumulative Update 2 [4] or
ii. 64-bit edition of Microsoft SQL Server 2005 with Service Pack 3 (SP3) [5] and Cumulative update package 3 for SQL Server 2005 Service Pack 3 [6] or
iii. Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2
iiiii. Service Accounts
Verify that you have the following service accounts created and their usernames and passwords available to you. Please visit the Microsoft website for more complete descriptions but below is a summary [10]:
1. SQL Server service account (account that SQL Server runs as)
a. Domain account
b. i.e. domainsvc-SQL2008Prod
2. Setup user account (account used for the install and configuration)
a. Domain user account
b. Member of the Administrators group on each server on which Setup is run (this is key!!) or Domain Administrator
c. SQL Server login on the computer that runs SQL Server
d. Member of the following SQL Server security roles:
i. securityadmin fixed server role
ii. dbcreator fixed server role
e. If you run Windows PowerShell cmdlets that affect a database, this account must be a member of the db_owner fixed database role for the database.
f. i.e. domainsp2010Admin
3. Content Access account (account used to crawl and build indexes)
a. Domain user account
b. i.e. domainsvc-SP2010Crawl
4. Server farm administrator account or database access account (account used to configure farm, timer service and Central Admin app pool identity)
a. Domain user account
b. i.e. domainsvc-SP2010Farm
c. On the main application server where you are installing SharePoint Central Admin, you should have this account set as a local administrator (*this is the only way I can get User Profile Synchronization to work – need to validate correct way to do this)
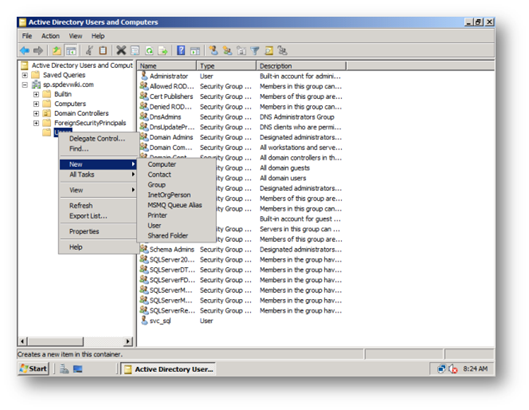
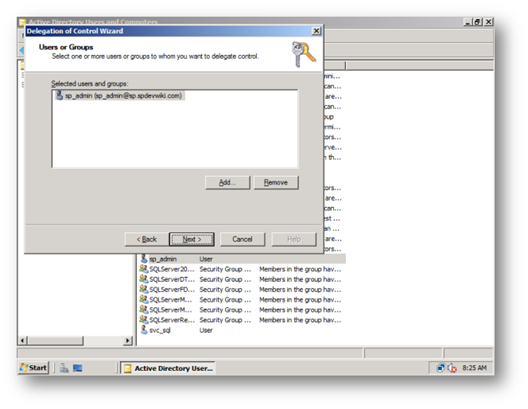
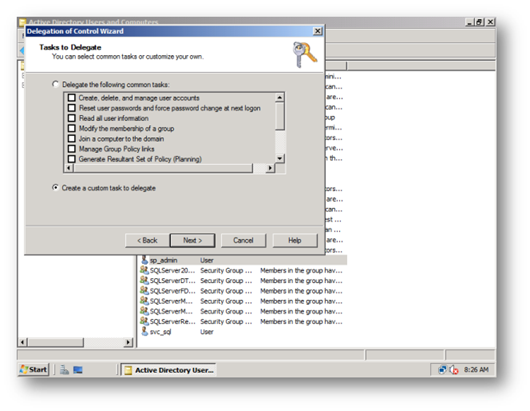
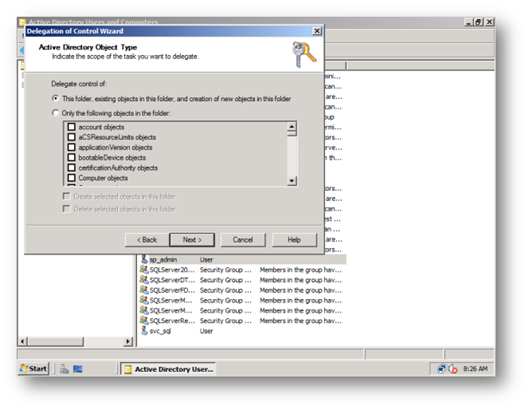
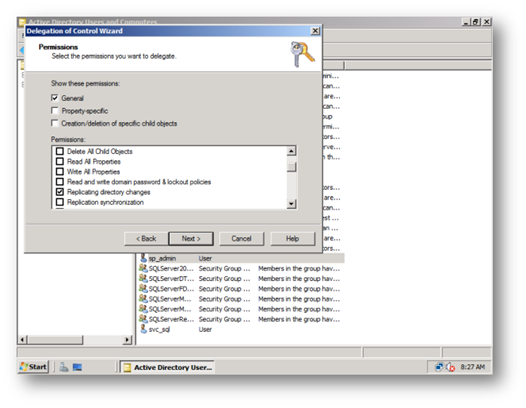
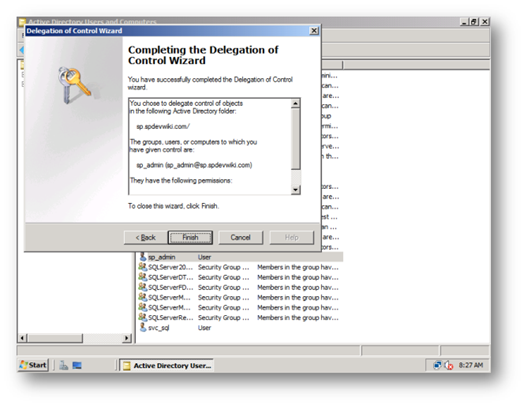
d. Ensure this account has Replicate Directory Changes on the Active Directory by performing the following – Great article on how to do this on sharepointdevwiki [11]
i. Login as a domain administrator on the AD Controller go to Active Directory Users and Computers, right click on the domain and Delegate Control to the farm service account to be able to replicate directory changes
iv. Miscellaneous Information
You should also have the following information on hand in order to be prepared for the configuration:
1. SMTP Server name (for outgoing email configuration)
2. SharePoint Administrator Email Address (for outgoing email configuration)
3. AD forest name (i.e. mydomain.com) and Domain Server DNS name (for setting up the user profile synchronization service). You can get this by typing in “nslookup” in command prompt from a computer on the domain
4. SQL Server Cluster DNS name. You should use a SQL Server cluster (active-passive or active-active) for your SQL Server and always reference this cluster name when configuring SharePoint
5. Load balanced DNS name(s). If you are for example adding two web servers to the farm that are load balanced (either through hardware or software), ensure that you have the DNS name for this load balanced url ready and configured to use (http://intranet.mydomain.com points to http://webserver1.mydomain.com and http://webserver2.mydomain.com with affinity off or on).
Click here to go the next part of this article – Installation Instructions